Automate Your Project with GitHub Models in Actions: AI Integration for Workflows
Authored by Kevin Lewis, this article explores practical ways to automate your GitHub Actions workflows using GitHub Models. It guides readers through permissions and shows AI-powered automation for triaging issues, summarizing pull requests, and more.
Automate Your Project with GitHub Models in Actions
Author: Kevin Lewis
Original post on The GitHub Blog
Overview
GitHub Models brings AI directly into GitHub Actions workflows, providing automation for tasks like triage, summarization, and more. This article offers a step-by-step guide on integrating GitHub Models within GitHub Actions, with three detailed workflow examples ranging from simple to advanced automation.
Getting Started: Permissions for GitHub Models
Before introducing AI to your workflows, ensure your workflows have the correct permissions; otherwise, AI calls will fail. Update your permissions block as follows:
permissions:
contents: read
issues: write
models: read
These permissions allow workflows to:
- Read repository content
- Read, create, or update issues and comments
- Access GitHub Models (AI features)
Example 1: Automating Bug Report Triage with AI Inference Action
Objective: Use AI to automatically assess new bug reports for sufficient information and respond if any is missing.
Workflow Setup:
- Create
.github/workflows/bug-reproduction-instructions.ymlin your repository. This workflow triggers on new issues.
name: Bug Report Reproduction Check
on:
issues:
types: [opened]
permissions:
contents: read
issues: write
models: read
jobs:
reproduction-steps-check:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Fetch Issue
id: issue
uses: actions/github-script@v7
with:
script: |
const issue = await github.rest.issues.get({
owner: context.repo.owner,
repo: context.repo.repo,
issue_number: context.issue.number
})
core.setOutput('title', issue.data.title)
core.setOutput('body', issue.data.body)
- Analyze issue reproducibility with the AI inference action (triggered if the issue is labeled ‘bug’).
- name: Analyze Issue For Reproduction
if: contains(join(github.event.issue.labels.*.name, ','), 'bug')
id: analyze-issue
uses: actions/ai-inference@v1
with:
model: mistral-ai/ministral-3b
system-prompt: |
Given a bug report title and text for an application, return 'pass' if there is enough information to reliably reproduce the issue...
prompt: |
Title: ${{ steps.issue.outputs.title }}
Body: ${{ steps.issue.outputs.body }}
- If the AI response is not ‘pass’, post a comment asking for missing details.
- name: Comment On Issue
if: contains(join(github.event.issue.labels.*.name, ','), 'bug') && steps.analyze-issue.outputs.response != 'pass'
uses: actions/github-script@v7
env:
AI_RESPONSE: steps.analyze-issue.outputs.response
with:
script: |
await github.rest.issues.createComment({
owner: context.repo.owner,
repo: context.repo.repo,
issue_number: context.issue.number,
body: process.env.AI_RESPONSE
})
Result: Issues with insufficient reproduction details are automatically flagged, requesting users to provide the missing information.
Example:
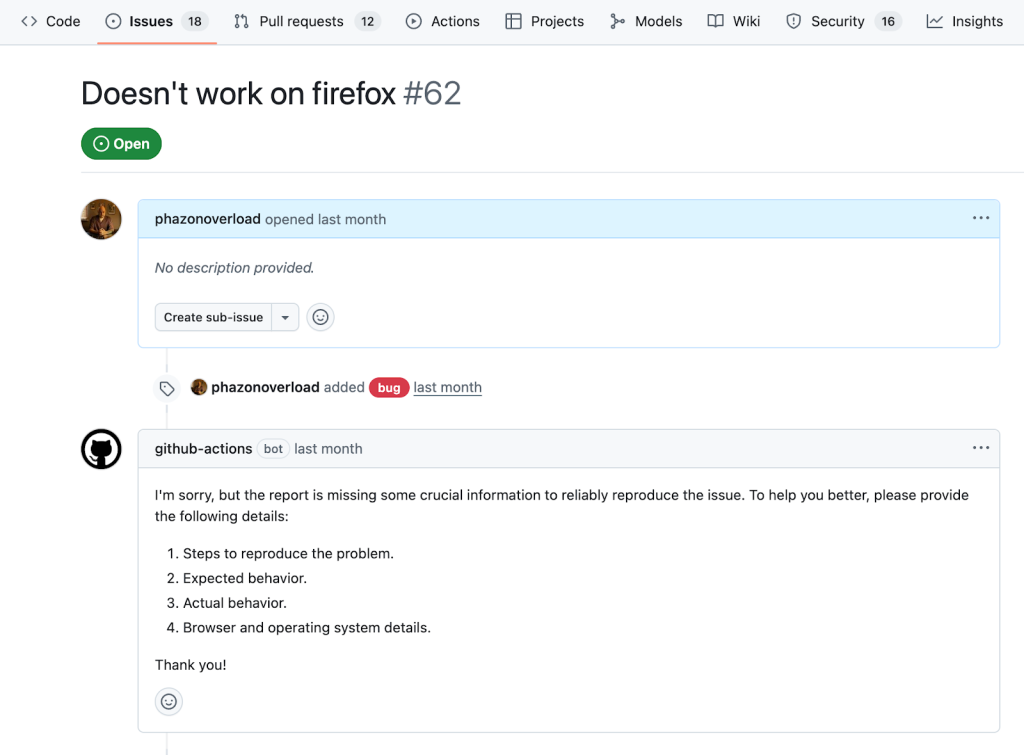
Example 2: Generating Release Notes from Merged Pull Requests
Objective: Automatically generate and append release notes from merged PRs using the GitHub CLI and gh-models extension.
Workflow Setup
- Create a ‘release’ label and an issue named ‘Publish next release changelog’ with this label.
- Add
.github/workflows/release-notes.ymlto your repository, which triggers when a pull request is closed.
name: Add to Changelog
on:
pull_request:
types: [closed]
permissions:
pull-requests: read
issues: write
contents: read
models: read
jobs:
add_to_changelog:
if: github.event.pull_request.merged == true
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- Install
gh-modelsCLI extension:
- name: Install gh-models extension
run: gh extension install https://github.com/github/gh-models
env:
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- Summarize the PR using an AI model and append summary to release issue:
PR_NUMBER="${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}"
# Fetch PR data
gh pr view "$PR_NUMBER" --json title,body,comments,reviews > pr.json
# AI-generated summary
cat pr.json | gh models run xai/grok-3-mini "...prompt..." > summary.md
# Get release issue
RELEASE_ISSUE=$(gh issue list --label release --limit 1 --json number --jq '.[0].number')
# Fetch and update release issue body
RELEASE_ISSUE_BODY=$(gh issue view "$RELEASE_ISSUE" --json body --jq '.body')
FORMATTED_LINE="- $(cat summary.md) (#$PR_NUMBER)"
NEW_BODY="${RELEASE_ISSUE_BODY}\n${FORMATTED_LINE}"
# Update issue
gh issue edit "$RELEASE_ISSUE" --body "$NEW_BODY"
Example:
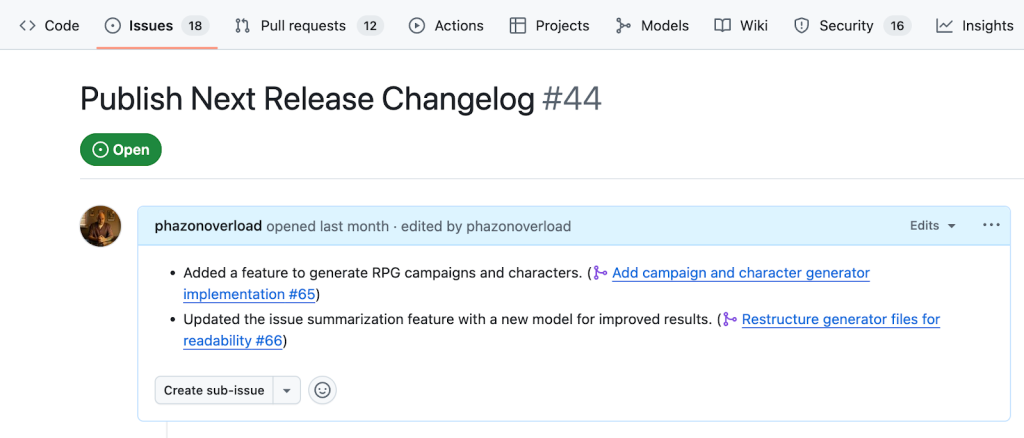
Example 3: Summarizing and Prioritizing Issues Weekly
Objective: Schedule a workflow to summarize, categorize, and prioritize issues from the past week.
Workflow Setup
- Add
.github/workflows/weekly-issue-summary.yml, scheduled for every Monday at 9 a.m.
name: Weekly Issue Summary
on:
workflow_dispatch:
schedule:
- cron: '0 9 * * 1'
permissions:
issues: write
contents: read
models: read
jobs:
create_weekly_summary:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install gh-models extension
run: gh extension install https://github.com/github/gh-models
env:
GH_TOKEN: ${{ github.token }}
- Gather open issues from the past week and summarize them with a prompt file:
LAST_WEEK=$(date -d "7 days ago" +"%Y-%m-%d")
gh search issues "created:>$LAST_WEEK" --state=open --json title,body,url --repo ${{ github.repository }} > issues.json
cat issues.json | gh models run --file prompts/issue-summary.prompt.yml > summary.md
The prompt file (prompts/issue-summary.prompt.yml):
name: Issue summarizer
description: Summarizes weekly issues
model: openai/gpt-4.1
messages:
- role: system
content: You are a helpful issue summarizer. When given issue content, respond in markdown format.
- role: user
content: "Please summarize the following issues into a few short bullet points. Include links if provided. If possible, pull out general themes and help the team prioritize based on impact. Issues begin here:\n "
- Create a new issue with the AI-generated summary:
ISSUE_TITLE="Issue Summary - $(date -d '7 days ago' '+%B %d') to $(date '+%B %d')"
gh issue create --title "$ISSUE_TITLE" --label summary --body-file summary.md
Example:
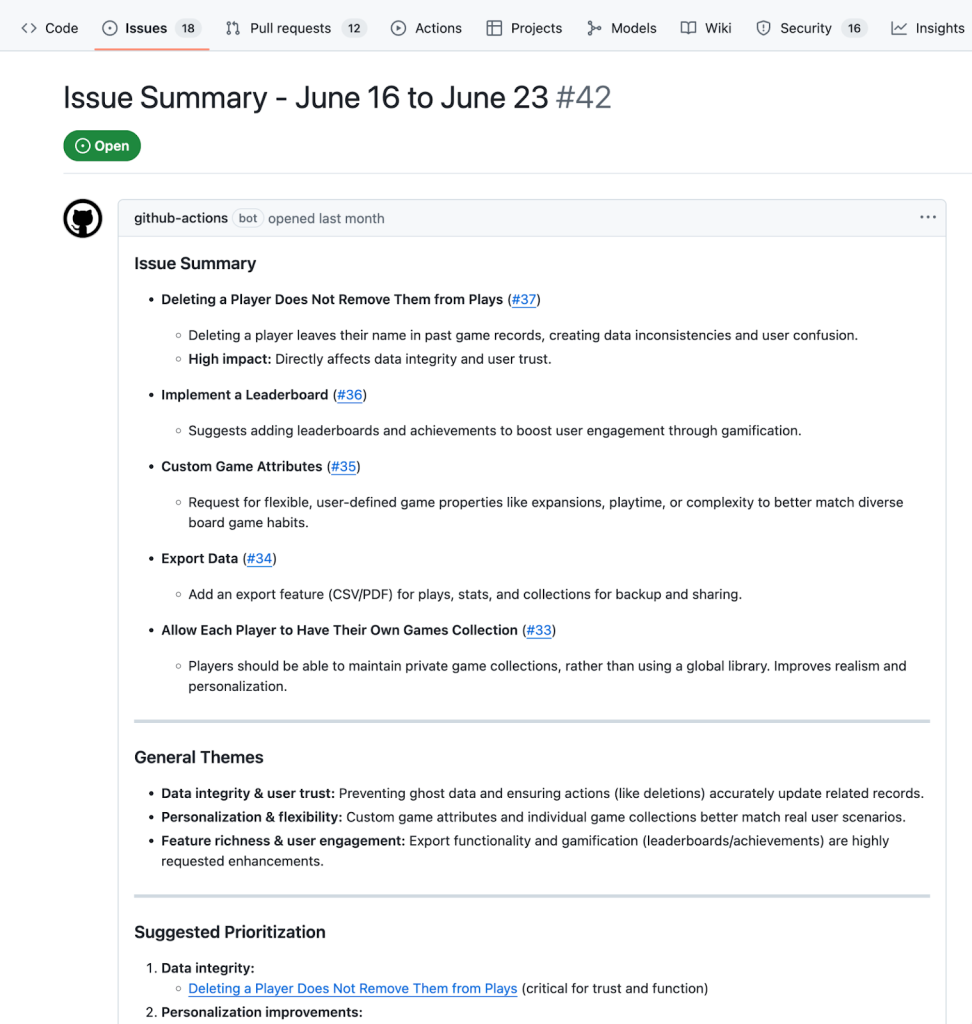
Conclusion
GitHub Models and GitHub Actions enable a rich set of possibilities for AI-driven workflow automation. By setting the right permissions and following the illustrated examples, teams can:
- Automate bug triage
- Generate and append release notes
- Summarize and prioritize issues
Explore the GitHub Models catalog and try integrating AI-powered features in your next workflow.
This post appeared first on “The GitHub Blog”. Read the entire article here