Enhancing Conversational Agents with Azure AI Language: CLU and Custom Question Answering
Authored by peytonfraser, this article provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in Azure AI Foundry’s conversational agent capabilities. It highlights new customization features in CLU and CQA and provides practical guidance for leveraging these tools in enterprise AI solutions.
Enhancing Conversational Agents with Azure AI Language: CLU and Custom Question Answering
Authored by peytonfraser
As part of ongoing efforts to empower the agent design experience, recent updates to Azure AI Foundry introduce several new features for developing conversational agents—most notably enhancements to Conversational Language Understanding (CLU) and Custom Question Answering (CQA). This article summarizes these advancements and provides guidance for utilizing them when building intelligent conversational systems.
Expanded Customization in AI Foundry
Conversational Language Understanding (CLU) and Custom Question Answering (CQA) are now fully integrated with AI Foundry. This integration allows developers and business stakeholders to fine-tune custom multilingual language models all within a unified user experience.
Key benefits include:
- Centralized management for Azure AI models
- Robust and efficient customization, from fine-tuning setup to deployment
- Support for multi-modal intelligence and multilingual scenarios
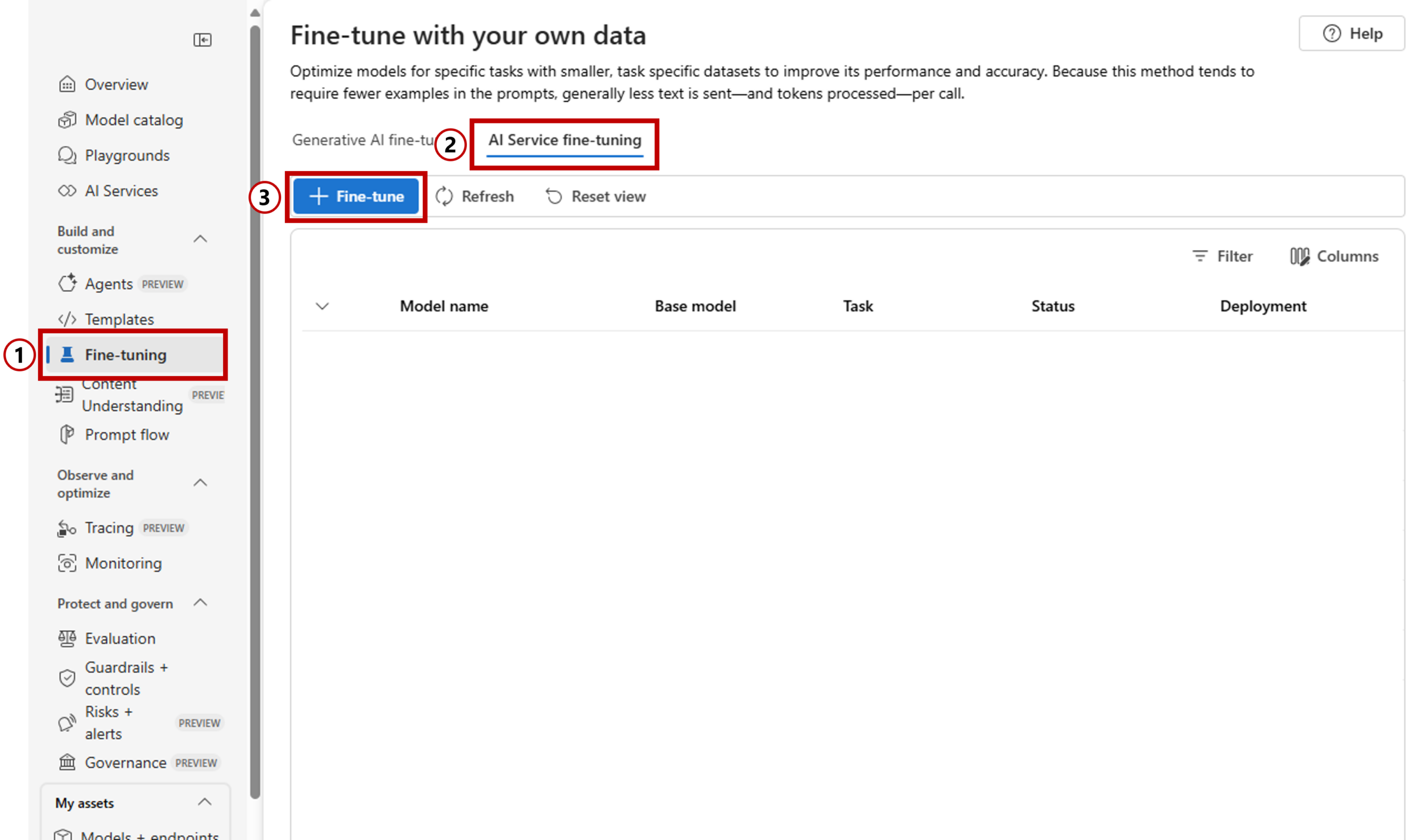
Figure 1 – Three easy steps for language fine-tuning in AI Foundry
Smart Intent Routing with CLU
The new Intent Triage Agent uses CLU to enable:
- Building custom natural language understanding models in over 100 languages
- Predicting user intent and extracting key information quickly
Deployment options now offered:
- Quick Deploy (Option #1):
- Deploy a CLU model by providing only a list of intents and brief descriptions—no traditional machine learning training required
- LLM-powered configuration delivers immediate functionality, with results accessible in structured JSON format
- Especially useful for rapid prototyping and broad topic coverage
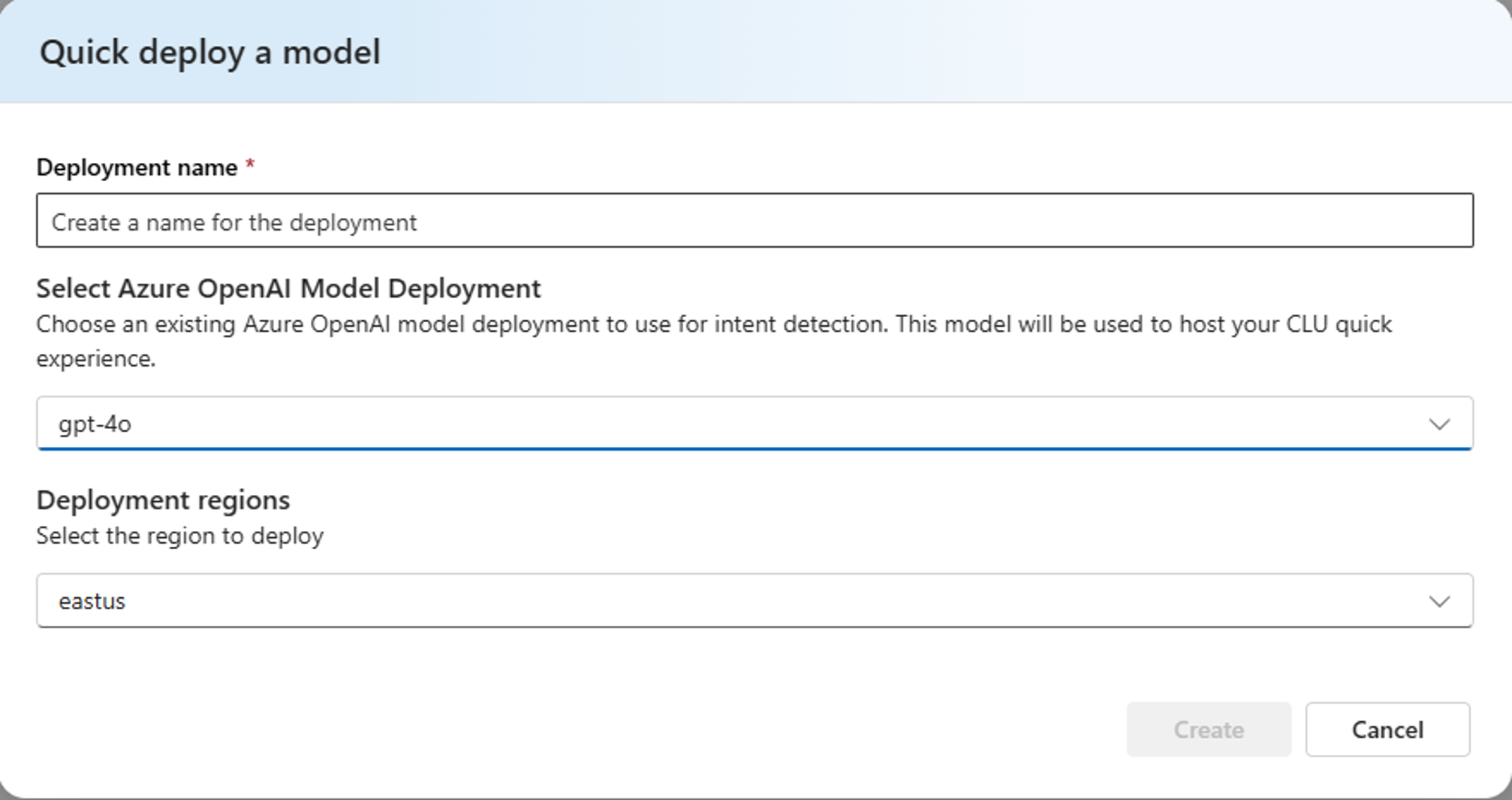
Figure 2 – Deploy CLU quickly with the power of LLMs in the new Quick Deploy feature
Tips for Quick Deploy:
- Ensure Cognitive Services User role assignment in Azure Portal for appropriate resource access
- Use clear, concise intent names (2-3 words; camelCase or underscore_separated)
- Add succinct, focused intent descriptions (50–100 characters recommended)
-
Optionally provide example utterances per intent to improve LLM predictions
- Customization with Machine Learning (Option #2):
- Offers detailed model training for context-specific, deterministic results
- Enables enhanced features: model performance evaluation, confidence scoring, on-premises container support, and entity recognition
- Suitable for production scenarios needing control over inference and prediction
Both deployment options allow users to preview predictions in the AI Foundry playground. This flexibility supports efficient, scalable intent routing for complex conversational flows.
Precision Question-Answering with CQA
The new Exact Question-Answering Agent leverages Custom Question Answering to:
- Build AI systems answering user queries precisely using content from documents, websites, or knowledge bases
- Tailor responses to specific business requirements
Recent enhancements include:
- Exact match answering for verbatim question/answer pairs, independent of scoring
- Support for the familiar QnA Maker scoring system, giving users algorithm and scoring flexibility
The improved CQA experience, available through the new AI Foundry portal, enables developers to create agents capable of understanding questions and providing confident, context-aware answers.
Resources and Further Reading
- For practical examples, refer to the Agent Template GitHub repo, intent triage agent, and exact question-answering agent.
- Additional documentation is available at Microsoft Learn.
- For the latest news, see the AI Foundry blog.
These updates help empower developers building Azure-based conversational agents to deliver clearer, more accurate, and efficient AI-driven interactions.
This post appeared first on “Microsoft DevBlog”. Read the entire article here